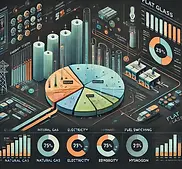
Energy Consumption Breakdown
Energy Breakdown of different configurations of flat glass decarbonisation
Energy Consumption and Emissions in Glass Furnaces
Glass production requires high-temperature furnaces to melt raw materials like silica, soda ash, and limestone. This analysis compares five furnace configurations based on energy consumption and CO₂ emissions:
-
NGfur (Natural Gas Furnace) – Conventional fossil fuel furnace
-
NGOxyfur (Oxy-Fuel Furnace) – Uses oxygen for efficient combustion
-
Hybfur (Hybrid Furnace) – Partial Electrification
-
ELfur (Electric Furnace) – All electric furnace
-
H2fur (Hydrogen Furnace) – Uses hydrogen as a clean fuel
Energy Demand Components (GJ/tCO₂)
-
Q-Process – Thermal energy for glass melting
-
EL-Process – Electrical demand for furnace operations
-
EL-ASU – Electricity for oxygen production in oxy-fuel systems
-
EL-CPU – Power required by cryogenic CO2 capture
-
EL-CCS – Power Required by MEA based Carbon Capture
-
Q-CCS – Heat Required by MEA based Carbon Capture
-
Heat Recovered – Waste heat recovered for CCS
-
Power Generated – On-site power generation from heat recovery
Carbon Capture (CCS) Impact
CCS increases energy demand due to CO₂ separation and compression but reduces overall direct and indirect emissions per ton of glass. This analysis highlights key decarbonization strategies in industrial glass manufacturing.